
Tan pi/2
The value of tan pi/2 is not defined. Tan pi/2 radians in degrees is written as tan ((π/2) × 180°/π), i.e., tan (90°). In this article, we will discuss the methods to find the value of tan pi/2 with examples.
- Tan pi/2: not defined
- Tan (-pi/2): not defined
- Tan pi/2 in degrees: tan (90°)
What is the Value of Tan pi/2?
The value of tan pi/2 is not defined. Tan pi/2 can also be expressed using the equivalent of the given angle (pi/2) in degrees (90°).
We know, using radian to degree conversion, θ in degrees = θ in radians × (180°/pi)
⇒ pi/2 radians = pi/2 × (180°/pi) = 90° or 90 degrees
∴ tan pi/2 = tan π/2 = tan(90°) = not defined
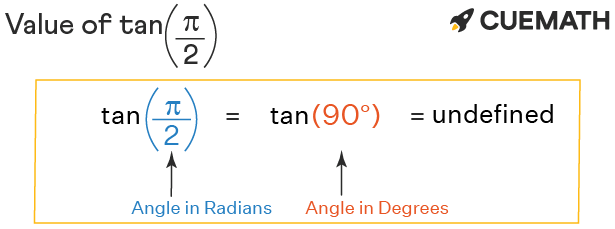
Explanation:
For tan pi/2, the angle pi/2 lies on the positive y-axis. Thus, tan pi/2 value = not defined
Since the tangent function is a periodic function, we can represent tan pi/2 as, tan pi/2 = tan(pi/2 + n × pi), n ∈ Z.
⇒ tan pi/2 = tan 3pi/2 = tan 5pi/2 , and so on.
Note: Since, tangent is an odd function, the value of tan(-pi/2) = -tan(pi/2) = undefined.
Methods to Find Value of Tan pi/2
The value of tan pi/2 is given as not defined. We can find the value of tan pi/2 by:
- Using Trigonometric Functions
- Using Unit Circle
Tan pi/2 in Terms of Trigonometric Functions
Using trigonometry formulas, we can represent the tan pi/2 as:
- sin(pi/2)/cos(pi/2)
- ± sin(pi/2)/√(1 - sin²(pi/2))
- ± √(1 - cos²(pi/2))/cos(pi/2)
- ± 1/√(cosec²(pi/2) - 1)
- ± √(sec²(pi/2) - 1)
- 1/cot(pi/2)
Note: Since pi/2 lies on the positive y-axis, the final value of tan pi/2 is not defined.
We can use trigonometric identities to represent tan pi/2 as,
- cot(pi/2 - pi/2) = cot 0
- -cot(pi/2 + pi/2) = -cot pi
- -tan (pi - pi/2) = -tan pi/2
Tan pi/2 Using Unit Circle
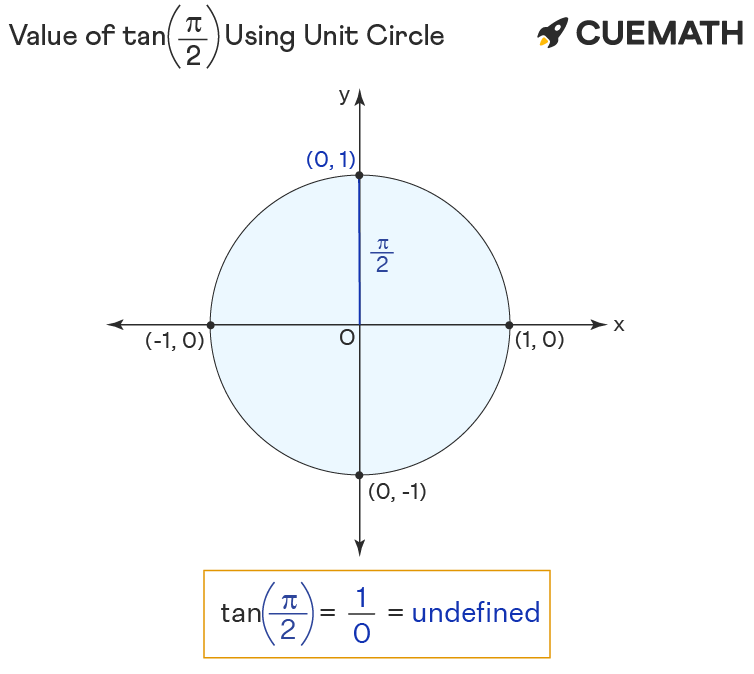
To find the value of tan π/2 using the unit circle:
- Rotate ‘r’ anticlockwise to form pi/2 angle with the positive x-axis.
- The tan of pi/2 equals the y-coordinate(1) divided by the x-coordinate(0) of the point of intersection (0, 1) of unit circle and r.
Hence the value of tan pi/2 = y/x = not defined
☛ Also Check:
Examples Using Tan pi/2
-
Example 1: Using the value of tan pi/2, solve: (sec²(pi/2) - 1).
Solution:
We know, (sec²(pi/2) - 1) = (tan²(pi/2)) = not defined
⇒ (sec²(pi/2) - 1) = not defined -
Example 2: Find the value of tan pi/2 if cot pi/2 is 0.
Solution:
Since, tan pi/2 = 1/cot(pi/2)
⇒ tan pi/2 = 1/0 = not defined -
Example 3: Find the value of 8 tan(pi/2)/10 tan(pi/4).
Solution:
Using trigonometric values, we know, tan(pi/2) = undefined and tan pi/4 = 1.
⇒ Value of 8 tan(pi/2)/10 tan(pi/4) = undefined

FAQs on Tan pi/2
What is Tan pi/2?
Tan pi/2 is the value of tangent trigonometric function for an angle equal to π/2 radians. The value of tan pi/2 is not defined.
What is the Exact Value of tan pi/2?
The exact value of tan pi/2 is not defined.
What is the Value of Tan pi/2 in Terms of Cot pi/2?
Since the tangent function is the reciprocal of the cotangent function, we can write tan pi/2 as 1/cot(pi/2). The value of cot pi/2 is equal to 0.
How to Find Tan pi/2 in Terms of Other Trigonometric Functions?
Using trigonometry formula, the value of tan pi/2 can be given in terms of other trigonometric functions as:
- sin(pi/2)/cos(pi/2)
- ± sin(pi/2)/√(1 - sin²(pi/2))
- ± √(1 - cos²(pi/2))/cos(pi/2)
- ± 1/√(cosec²(pi/2) - 1)
- ± √(sec²(pi/2) - 1)
- 1/cot(pi/2)
☛ Also check: trigonometric table
How to Find the Value of Tan pi/2?
The value of tan pi/2 can be calculated by constructing an angle of π/2 radians with the x-axis, and then finding the coordinates of the corresponding point (0, 1) on the unit circle. The value of tan pi/2 is equal to the y-coordinate(1) divided by the x-coordinate (0). ∴ tan pi/2 = not defined
visual curriculum