Sin 150 Degrees
The value of sin 150 degrees is 0.5. Sin 150 degrees in radians is written as sin (150° × π/180°), i.e., sin (5π/6) or sin (2.617993. . .). In this article, we will discuss the methods to find the value of sin 150 degrees with examples.
- Sin 150°: 0.5
- Sin 150° in fraction: 1/2
- Sin (-150 degrees): -0.5
- Sin 150° in radians: sin (5π/6) or sin (2.6179938 . . .)
What is the Value of Sin 150 Degrees?
The value of sin 150 degrees in decimal is 0.5. Sin 150 degrees can also be expressed using the equivalent of the given angle (150 degrees) in radians (2.61799 . . .).
We know, using degree to radian conversion, θ in radians = θ in degrees × (pi/180°)
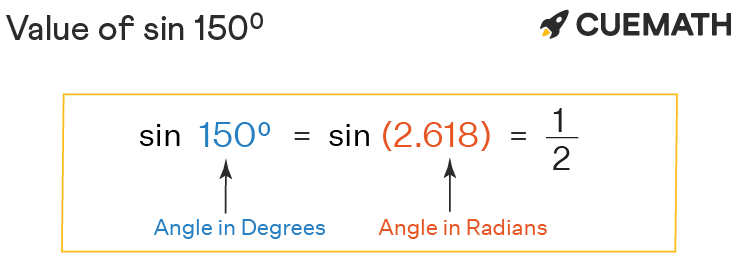
⇒ 150 degrees = 150° × (π/180°) rad = 5π/6 or 2.6179 . . .
∴ sin 150° = sin(2.6179) = 1/2 or 0.5
Explanation:
For sin 150 degrees, the angle 150° lies between 90° and 180° (Second Quadrant). Since sine function is positive in the second quadrant, thus sin 150° value = 1/2 or 0.5
Since the sine function is a periodic function, we can represent sin 150° as, sin 150 degrees = sin(150° + n × 360°), n ∈ Z.
⇒ sin 150° = sin 510° = sin 870°, and so on.
Note: Since, sine is an odd function, the value of sin(-150°) = -sin(150°).
Methods to Find Value of Sin 150 Degrees
The sine function is positive in the 2nd quadrant. The value of sin 150° is given as 0.5. We can find the value of sin 150 degrees by:
- Using Unit Circle
- Using Trigonometric Functions
Sin 150 Degrees Using Unit Circle
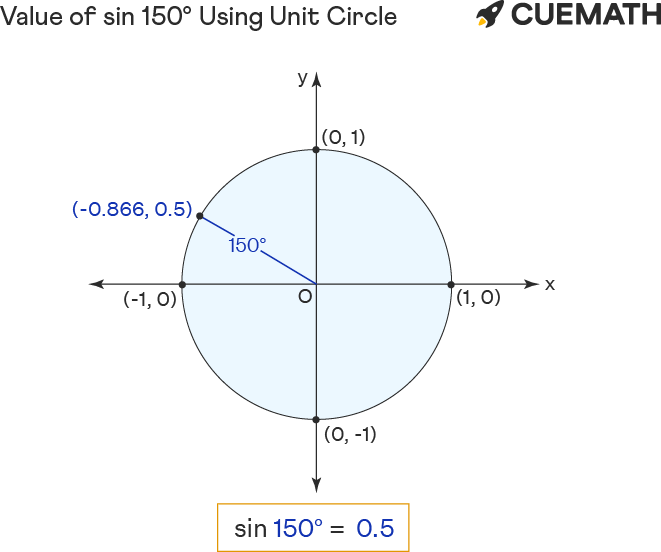
To find the value of sin 150 degrees using the unit circle:
- Rotate ‘r’ anticlockwise to form a 150° angle with the positive x-axis.
- The sin of 150 degrees equals the y-coordinate(0.5) of the point of intersection (-0.866, 0.5) of unit circle and r.
Hence the value of sin 150° = y = 0.5
Sin 150° in Terms of Trigonometric Functions
Using trigonometry formulas, we can represent the sin 150 degrees as:
- ± √(1-cos²(150°))
- ± tan 150°/√(1 + tan²(150°))
- ± 1/√(1 + cot²(150°))
- ± √(sec²(150°) - 1)/sec 150°
- 1/cosec 150°
Note: Since 150° lies in the 2nd Quadrant, the final value of sin 150° will be positive.
We can use trigonometric identities to represent sin 150° as,
- sin(180° - 150°) = sin 30°
- -sin(180° + 150°) = -sin 330°
- cos(90° - 150°) = cos(-60°)
- -cos(90° + 150°) = -cos 240°
☛ Also Check:
Examples Using Sin 150 Degrees
-
Example 1: Find the value of 2 × (sin 75° cos 75°). [Hint: Use sin 150° = 0.5]
Solution:
Using the sin 2a formula,
2 sin 75° cos 75° = sin(2 × 75°) = sin 150°
∵ sin 150° = 0.5
⇒ 2 × (sin 75° cos 75°) = 0.5 -
Example 2: Simplify: 2 (sin 150°/sin 510°)
Solution:
We know sin 150° = sin 510°
⇒ 2 sin 150°/sin 510° = 2(sin 150°/sin 150°)
= 2(1) = 2 -
Example 3: Find the value of 5 sin(150°)/7 cos(-60°).
Solution:
Using trigonometric identities, we know, sin(150°) = cos(90° - 150°) = cos(-60°).
⇒ sin(150°) = cos(-60°)
⇒ Value of 5 sin(150°)/7 cos(-60°) = 5/7

FAQs on Sin 150 Degrees
What is Sin 150 Degrees?
Sin 150 degrees is the value of sine trigonometric function for an angle equal to 150 degrees. The value of sin 150° is 1/2 or 0.5.
What is the Value of Sin 150° in Terms of Cosec 150°?
Since the cosecant function is the reciprocal of the sine function, we can write sin 150° as 1/cosec(150°). The value of cosec 150° is equal to 2.
How to Find Sin 150° in Terms of Other Trigonometric Functions?
Using trigonometry formula, the value of sin 150° can be given in terms of other trigonometric functions as:
- ± √(1-cos²(150°))
- ± tan 150°/√(1 + tan²(150°))
- ± 1/√(1 + cot²(150°))
- ± √(sec²(150°) - 1)/sec 150°
- 1/cosec 150°
☛ Also check: trigonometric table
How to Find the Value of Sin 150 Degrees?
The value of sin 150 degrees can be calculated by constructing an angle of 150° with the x-axis, and then finding the coordinates of the corresponding point (-0.866, 0.5) on the unit circle. The value of sin 150° is equal to the y-coordinate (0.5). ∴ sin 150° = 0.5.
What is the Value of Sin 150 Degrees in Terms of Cos 150°?
Using trigonometric identities, we can write sin 150° in terms of cos 150° as, sin(150°) = √(1-cos²(150°)). Here, the value of cos 150° is equal to −√3/2.
visual curriculum