How to find the domain of a function on a graph?
The domain of a function is defined as the set of all possible input values.
Answer: A domain is the set of ‘all the values’ that go into a function. The domain of a function is all the possible values of the independent variable x, for which y is defined.
Let's understand the domain.
Explanation:
A domain is ‘all the values’ that go into a function. The domain of a function is all the possible values of the independent variable x, for which y is defined. The range of a function is all the possible output values of the function.
Finding Domain:
In a given ordered pair (x,y), the domain is defined as the set of all first elements of ordered pairs (x-coordinates). Thus, on a graph, the domain can be found by the set of values towards the direction of the x-axis.
Let's take an example to understand the calculation of domain.
Example: Find the domain of the function given below.
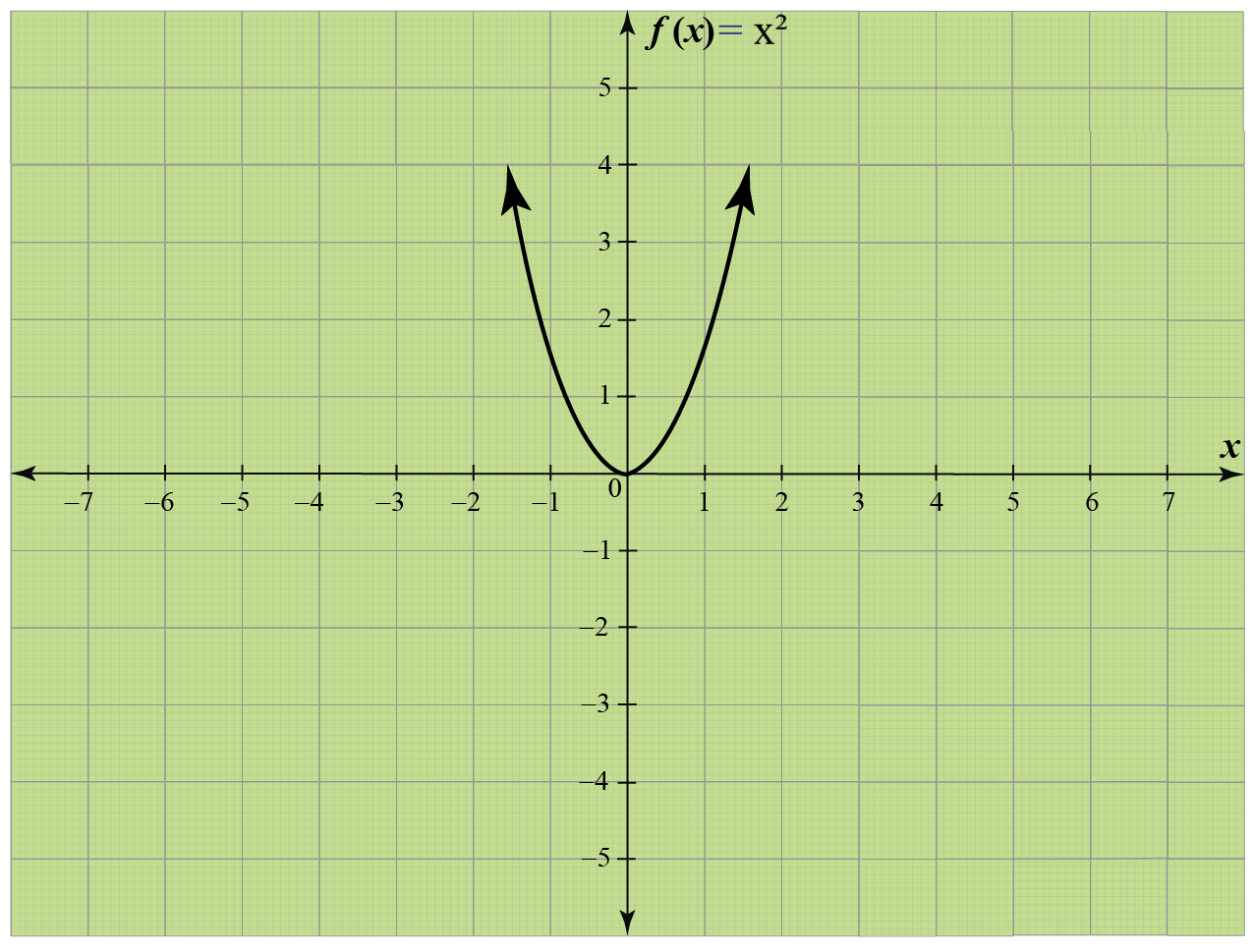
Solution:
We observe from the graph that the horizontal extent of the graph is from (−∞,∞).
So, the domain is (−∞,∞).
Thus, for a quadratic function f(x) = x2, the domain is all real numbers.
Hence, the domain of the given function graph is (−∞,∞).
visual curriculum
