LCM of 8, 12, and 16
LCM of 8, 12, and 16 is the smallest number among all common multiples of 8, 12, and 16. The first few multiples of 8, 12, and 16 are (8, 16, 24, 32, 40 . . .), (12, 24, 36, 48, 60 . . .), and (16, 32, 48, 64, 80 . . .) respectively. There are 3 commonly used methods to find LCM of 8, 12, 16 - by listing multiples, by division method, and by prime factorization.
| 1. | LCM of 8, 12, and 16 |
| 2. | List of Methods |
| 3. | Solved Examples |
| 4. | FAQs |
What is the LCM of 8, 12, and 16?
Answer: LCM of 8, 12, and 16 is 48.

Explanation:
The LCM of three non-zero integers, a(8), b(12), and c(16), is the smallest positive integer m(48) that is divisible by a(8), b(12), and c(16) without any remainder.
Methods to Find LCM of 8, 12, and 16
The methods to find the LCM of 8, 12, and 16 are explained below.
- By Division Method
- By Listing Multiples
- By Prime Factorization Method
LCM of 8, 12, and 16 by Division Method
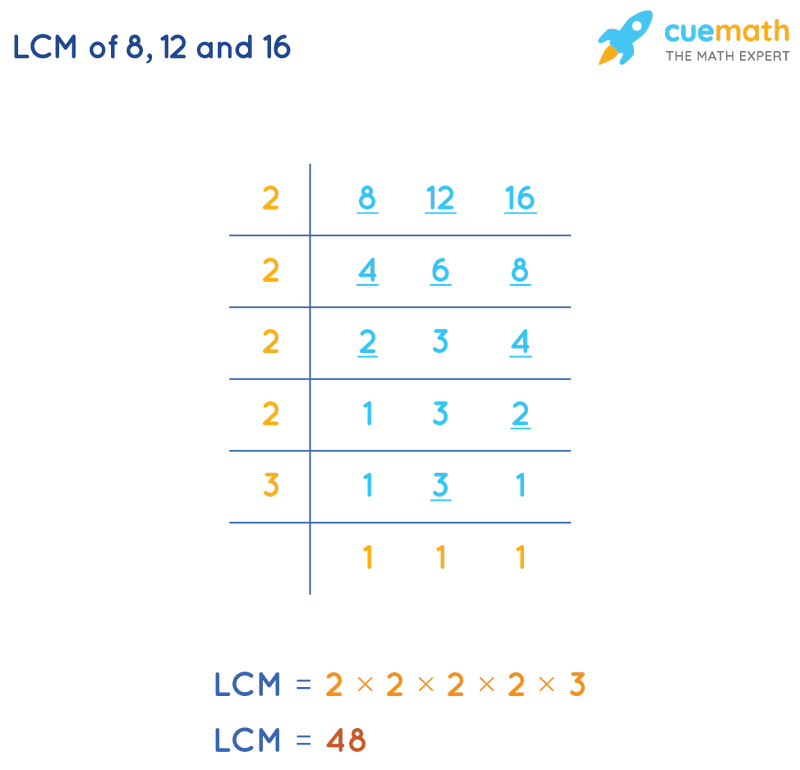
To calculate the LCM of 8, 12, and 16 by the division method, we will divide the numbers(8, 12, 16) by their prime factors (preferably common). The product of these divisors gives the LCM of 8, 12, and 16.
- Step 1: Find the smallest prime number that is a factor of at least one of the numbers, 8, 12, and 16. Write this prime number(2) on the left of the given numbers(8, 12, and 16), separated as per the ladder arrangement.
- Step 2: If any of the given numbers (8, 12, 16) is a multiple of 2, divide it by 2 and write the quotient below it. Bring down any number that is not divisible by the prime number.
- Step 3: Continue the steps until only 1s are left in the last row.
The LCM of 8, 12, and 16 is the product of all prime numbers on the left, i.e. LCM(8, 12, 16) by division method = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 = 48.
LCM of 8, 12, and 16 by Listing Multiples
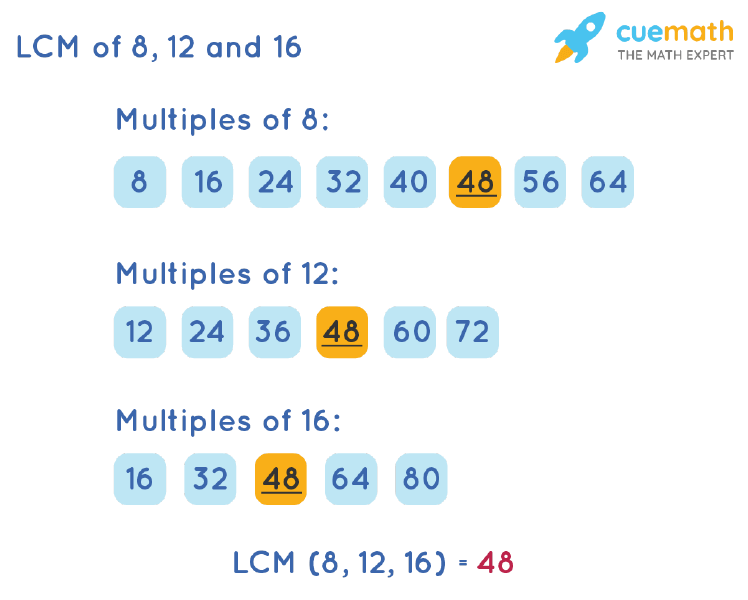
To calculate the LCM of 8, 12, 16 by listing out the common multiples, we can follow the given below steps:
- Step 1: List a few multiples of 8 (8, 16, 24, 32, 40 . . .), 12 (12, 24, 36, 48, 60 . . .), and 16 (16, 32, 48, 64, 80 . . .).
- Step 2: The common multiples from the multiples of 8, 12, and 16 are 48, 96, . . .
- Step 3: The smallest common multiple of 8, 12, and 16 is 48.
∴ The least common multiple of 8, 12, and 16 = 48.
LCM of 8, 12, and 16 by Prime Factorization
Prime factorization of 8, 12, and 16 is (2 × 2 × 2) = 23, (2 × 2 × 3) = 22 × 31, and (2 × 2 × 2 × 2) = 24 respectively. LCM of 8, 12, and 16 can be obtained by multiplying prime factors raised to their respective highest power, i.e. 24 × 31 = 48.
Hence, the LCM of 8, 12, and 16 by prime factorization is 48.
☛ Also Check:
- LCM of 3 and 12 - 12
- LCM of 16 and 22 - 176
- LCM of 2 and 5 - 10
- LCM of 10 and 15 - 30
- LCM of 1 and 5 - 5
- LCM of 8 and 15 - 120
- LCM of 186 and 403 - 2418
LCM of 8, 12, and 16 Examples
-
Example 1: Calculate the LCM of 8, 12, and 16 using the GCD of the given numbers.
Solution:
Prime factorization of 8, 12, 16:
- 8 = 23
- 12 = 22 × 31
- 16 = 24
Therefore, GCD(8, 12) = 4, GCD(12, 16) = 4, GCD(8, 16) = 8, GCD(8, 12, 16) = 4
We know,
LCM(8, 12, 16) = [(8 × 12 × 16) × GCD(8, 12, 16)]/[GCD(8, 12) × GCD(12, 16) × GCD(8, 16)]
LCM(8, 12, 16) = (1536 × 4)/(4 × 4 × 8) = 48
⇒LCM(8, 12, 16) = 48 -
Example 2: Verify the relationship between the GCD and LCM of 8, 12, and 16.
Solution:
The relation between GCD and LCM of 8, 12, and 16 is given as,
LCM(8, 12, 16) = [(8 × 12 × 16) × GCD(8, 12, 16)]/[GCD(8, 12) × GCD(12, 16) × GCD(8, 16)]
⇒ Prime factorization of 8, 12 and 16:- 8 = 23
- 12 = 22 × 31
- 16 = 24
∴ GCD of (8, 12), (12, 16), (8, 16) and (8, 12, 16) = 4, 4, 8 and 4 respectively.
Now, LHS = LCM(8, 12, 16) = 48.
And, RHS = [(8 × 12 × 16) × GCD(8, 12, 16)]/[GCD(8, 12) × GCD(12, 16) × GCD(8, 16)] = [(1536) × 4]/[4 × 4 × 8] = 48
LHS = RHS = 48.
Hence verified. -
Example 3: Find the smallest number that is divisible by 8, 12, 16 exactly.
Solution:
The smallest number that is divisible by 8, 12, and 16 exactly is their LCM.
⇒ Multiples of 8, 12, and 16:- Multiples of 8 = 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, . . . .
- Multiples of 12 = 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 84, . . . .
- Multiples of 16 = 16, 32, 48, 64, 80, 96, 112, . . . .
Therefore, the LCM of 8, 12, and 16 is 48.

FAQs on LCM of 8, 12, and 16
What is the LCM of 8, 12, and 16?
The LCM of 8, 12, and 16 is 48. To find the least common multiple (LCM) of 8, 12, and 16, we need to find the multiples of 8, 12, and 16 (multiples of 8 = 8, 16, 24, 32, 48 . . . .; multiples of 12 = 12, 24, 36, 48 . . . .; multiples of 16 = 16, 32, 48, 64 . . . .) and choose the smallest multiple that is exactly divisible by 8, 12, and 16, i.e., 48.
Which of the following is the LCM of 8, 12, and 16? 11, 81, 48, 36
The value of LCM of 8, 12, 16 is the smallest common multiple of 8, 12, and 16. The number satisfying the given condition is 48.
What is the Relation Between GCF and LCM of 8, 12, 16?
The following equation can be used to express the relation between GCF and LCM of 8, 12, 16, i.e. LCM(8, 12, 16) = [(8 × 12 × 16) × GCF(8, 12, 16)]/[GCF(8, 12) × GCF(12, 16) × GCF(8, 16)].
How to Find the LCM of 8, 12, and 16 by Prime Factorization?
To find the LCM of 8, 12, and 16 using prime factorization, we will find the prime factors, (8 = 23), (12 = 22 × 31), and (16 = 24). LCM of 8, 12, and 16 is the product of prime factors raised to their respective highest exponent among the numbers 8, 12, and 16.
⇒ LCM of 8, 12, 16 = 24 × 31 = 48.
visual curriculum