GCF of 45 and 76
GCF of 45 and 76 is the largest possible number that divides 45 and 76 exactly without any remainder. The factors of 45 and 76 are 1, 3, 5, 9, 15, 45 and 1, 2, 4, 19, 38, 76 respectively. There are 3 commonly used methods to find the GCF of 45 and 76 - long division, Euclidean algorithm, and prime factorization.
| 1. | GCF of 45 and 76 |
| 2. | List of Methods |
| 3. | Solved Examples |
| 4. | FAQs |
What is GCF of 45 and 76?
Answer: GCF of 45 and 76 is 1.

Explanation:
The GCF of two non-zero integers, x(45) and y(76), is the greatest positive integer m(1) that divides both x(45) and y(76) without any remainder.
Methods to Find GCF of 45 and 76
Let's look at the different methods for finding the GCF of 45 and 76.
- Long Division Method
- Using Euclid's Algorithm
- Listing Common Factors
GCF of 45 and 76 by Long Division
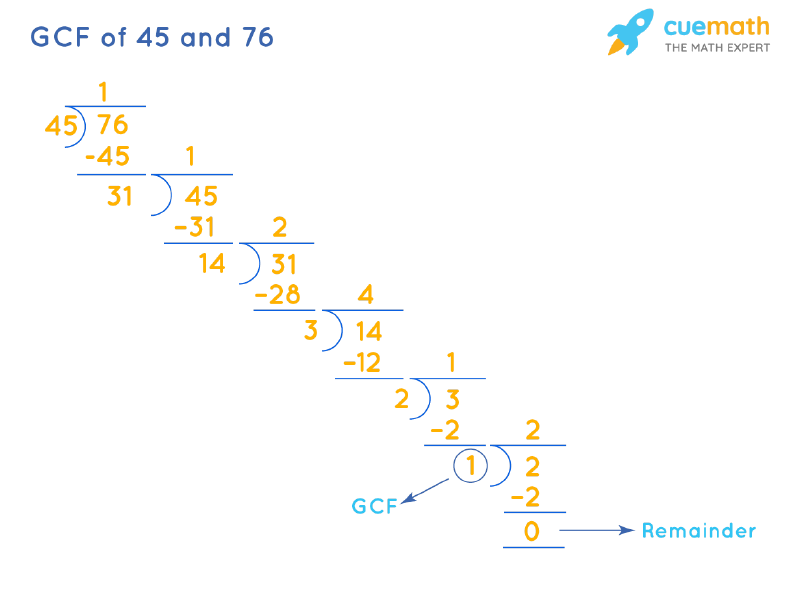
GCF of 45 and 76 is the divisor that we get when the remainder becomes 0 after doing long division repeatedly.
- Step 1: Divide 76 (larger number) by 45 (smaller number).
- Step 2: Since the remainder ≠ 0, we will divide the divisor of step 1 (45) by the remainder (31).
- Step 3: Repeat this process until the remainder = 0.
The corresponding divisor (1) is the GCF of 45 and 76.
GCF of 45 and 76 by Euclidean Algorithm
As per the Euclidean Algorithm, GCF(X, Y) = GCF(Y, X mod Y)
where X > Y and mod is the modulo operator.
Here X = 76 and Y = 45
- GCF(76, 45) = GCF(45, 76 mod 45) = GCF(45, 31)
- GCF(45, 31) = GCF(31, 45 mod 31) = GCF(31, 14)
- GCF(31, 14) = GCF(14, 31 mod 14) = GCF(14, 3)
- GCF(14, 3) = GCF(3, 14 mod 3) = GCF(3, 2)
- GCF(3, 2) = GCF(2, 3 mod 2) = GCF(2, 1)
- GCF(2, 1) = 1 (∵ GCF(X, 1) = 1)
Therefore, the value of GCF of 45 and 76 is 1.
GCF of 45 and 76 by Listing Common Factors
- Factors of 45: 1, 3, 5, 9, 15, 45
- Factors of 76: 1, 2, 4, 19, 38, 76
Since, 1 is the only common factor between 45 and 76. The Greatest Common Factor of 45 and 76 is 1.
☛ Also Check:
- GCF of 14 and 49 = 7
- GCF of 36 and 99 = 9
- GCF of 36 and 81 = 9
- GCF of 4 and 12 = 4
- GCF of 30 and 50 = 10
- GCF of 30 and 48 = 6
- GCF of 15 and 50 = 5
GCF of 45 and 76 Examples
-
Example 1: The product of two numbers is 3420. If their GCF is 1, what is their LCM?
Solution:
Given: GCF = 1 and product of numbers = 3420
∵ LCM × GCF = product of numbers
⇒ LCM = Product/GCF = 3420/1
Therefore, the LCM is 3420. -
Example 2: Find the GCF of 45 and 76, if their LCM is 3420.
Solution:
∵ LCM × GCF = 45 × 76
⇒ GCF(45, 76) = (45 × 76)/3420 = 1
Therefore, the greatest common factor of 45 and 76 is 1. -
Example 3: For two numbers, GCF = 1 and LCM = 3420. If one number is 45, find the other number.
Solution:
Given: GCF (z, 45) = 1 and LCM (z, 45) = 3420
∵ GCF × LCM = 45 × (z)
⇒ z = (GCF × LCM)/45
⇒ z = (1 × 3420)/45
⇒ z = 76
Therefore, the other number is 76.

FAQs on GCF of 45 and 76
What is the GCF of 45 and 76?
The GCF of 45 and 76 is 1. To calculate the greatest common factor of 45 and 76, we need to factor each number (factors of 45 = 1, 3, 5, 9, 15, 45; factors of 76 = 1, 2, 4, 19, 38, 76) and choose the greatest factor that exactly divides both 45 and 76, i.e., 1.
What is the Relation Between LCM and GCF of 45, 76?
The following equation can be used to express the relation between LCM and GCF of 45 and 76, i.e. GCF × LCM = 45 × 76.
How to Find the GCF of 45 and 76 by Prime Factorization?
To find the GCF of 45 and 76, we will find the prime factorization of the given numbers, i.e. 45 = 3 × 3 × 5; 76 = 2 × 2 × 19.
⇒ There is no common prime factor for 45 and 76. Hence, GCF (45, 76) = 1.
☛ Prime Number
What are the Methods to Find GCF of 45 and 76?
There are three commonly used methods to find the GCF of 45 and 76.
- By Long Division
- By Euclidean Algorithm
- By Prime Factorization
If the GCF of 76 and 45 is 1, Find its LCM.
GCF(76, 45) × LCM(76, 45) = 76 × 45
Since the GCF of 76 and 45 = 1
⇒ 1 × LCM(76, 45) = 3420
Therefore, LCM = 3420
☛ Greatest Common Factor Calculator
How to Find the GCF of 45 and 76 by Long Division Method?
To find the GCF of 45, 76 using long division method, 76 is divided by 45. The corresponding divisor (1) when remainder equals 0 is taken as GCF.
visual curriculum
