Additive Identity of Whole Number
Additive identity of whole number is defined as the addition of that number to the given whole number which doesn't alter its value mathematically. The additive identity of whole number is zero (0). We will be studying more about additive identity and additive property of whole numbers in this article.
| 1. | What is Additive Identity of Whole Number? |
| 2. | Additive Property of Whole Numbers |
| 3. | FAQs on Additive Identity of Whole Number |
What is Additive Identity of Whole Number?
The additive identity of whole number is 0. The term additive identity signifies that the number's identity is retained even after a certain operation has taken place. Here, the arithmetic operation that we perform is the addition operation. We know that, when 0 is added to any quantity, we get back the same result and there is no change in the value. We can also assume the identity element to be a mirror of this whole number as the number before and after the addition operation remains the same. Based on this fact we say that 0 is the identity element of the addition of whole numbers or simply known as the additive identity of whole numbers. Let's assume any whole number a. Then, we can say that a + 0 = a. For example, for the whole number 12, the additive identity is shown as 12 + 0 = 12.
Additive Property of Whole Numbers
The additive property of whole numbers is another name given to the additive identity of whole numbers. It means that, whenever the whole number is added to its identity element, its identity remains unchanged. We know that the identity element for whole numbers is 0 i.e., when any whole number is added to 0, we get back the number itself. For example, let's assume a whole number 67. We know that 67 + 0 = 67. Thus, we can observe that when the identity element 0 is added to the whole number 67, we get back the same number i.e., 67. The additive property of whole numbers is also known as the property of zero or zero property of whole numbers.
For a whole number x, the additive property states that x + 0 = 0 + x = x.
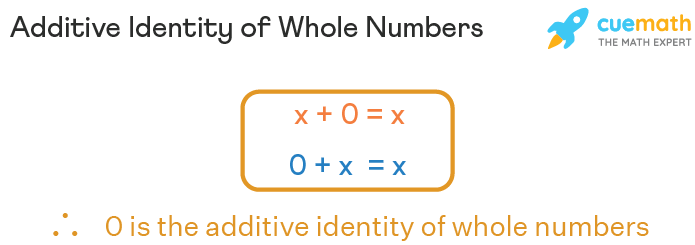
Just like the additive property of whole numbers, we also have the subtractive property of whole numbers also termed as subtractive property of zero. The arithmetic operation performed in this is the subtraction operation. We know that, when 0 is subtracted from any number, we get back the same number as the result. However, for a whole number 'a', a - 0 = a but 0 - a = - a. Thus, 0 does not satisfy the condition 0 - a, as we do not get back the same result. For example, for the whole number 23, when 0 is subtracted from 23, we get back the same number i.e., 23 - 0 = 23 but 0 - 23 = - 23 which doesn't give the same value. Therefore, 0 is not the identity element of subtraction of whole numbers.
Thus, for a whole number y, the subtractive property states that y - 0 = y.
Related Articles
Check the following articles that are related to the additive identity of whole numbers.
Additive Identity of Whole Number Examples
-
Example 1: Which of the following equation is an example of the additive identity of whole number?
a) 55 + 0 = 55
b) 100 + 7 = 107Solution: The first equation 55 + 0 = 55 is an example of the additive identity of the whole number as 55 is a whole number that is added to its identity element 0 to give back the same number 55.
The second equation 100 + 7 = 107 is not an example of the additive identity of the whole number since 100 is not being added to its identity element 0.
-
Example 2: There are 27 pastries in a container. No more pastries can fit in the container. Find the number of pastries in the container using the additive identity of whole number.
Solution: Given that after filling 27 pastries in the container, there is no space left to accommodate any more pastries. Thus, the number of pastries remains the same that is 27. By the additive property of the whole number, this can be shown as 27 pastries + 0 = 27 pastries.

FAQs on Additive Identity of Whole Number
What is Additive Identity of Whole Number?
The additive identity of whole numbers is equal to zero (0).
What is the Additive Identity Element in the Set of Whole Numbers?
The additive identity element in the set of whole numbers is 0 because when 0 is added to any whole number, it gives back the same number.
What is the Multiplicative and Additive Identity of Whole Numbers?
The multiplicative identity of whole numbers is equal to 1 and the additive identity of whole numbers is 0.
What is the Sum of Multiplicative Identity and Additive Identity of a Whole Number?
The multiplicative identity and additive identity of whole numbers are equal to 1 and 0 respectively. The sum of multiplicative identity and additive identity of the whole numbers is equal to 1 + 0 = 1.
What do we get when we Add the Additive Identity to a Whole Number?
When we add additive identity 0 to a whole number, we get back the same result. For example, 2 + 0 = 2.
visual curriculum
