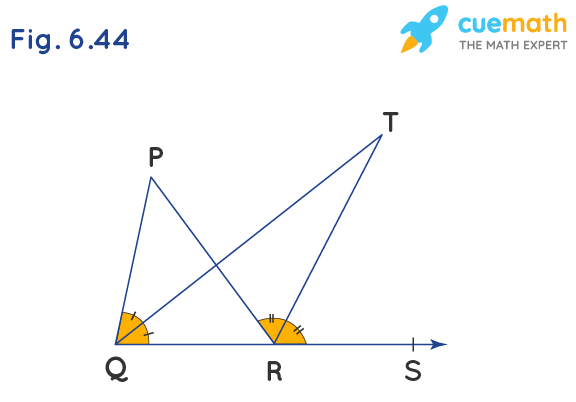
In Fig. 6.44, the side QR of △PQR is produced to a point S. If the bisectors of ∠PQR and ∠PRS meet at point T, then prove that ∠QTR = 1/2 ∠QPR
Solution:
Given: TQ and TR are the bisectors of ∠PQR and ∠PRS respectively
To Prove: ∠QTR = 1/2 ∠QPR
According to the exterior angle theorem of a triangle, if a side of a triangle is produced, then the exterior angle so formed is equal to the sum of the two interior opposite angles.
∠PRS = 2∠TRS.......(i) [Since TR is the angle bisector of ∠PRS]
∠PQR = 2∠TQR .........(ii) [Since TQ is the angle bisector of ∠PQR]
Now, in △TQR
∠TRS = ∠TQR +∠QTR [Exterior angle theorem of a triangle]
∠QTR = ∠TRS - ∠TQR.......... (iii)
Similarly, in △PQR
∠PRS = ∠QPR + ∠PQR [Exterior angle theorem of a triangle]
2∠TRS = ∠QPR + 2∠TQR [From (i) and (ii)]
∠QPR = 2∠TRS - 2∠TQR
∠QPR = 2(∠TRS - ∠TQR)
∠QPR = 2∠QTR [From (iii)]
∠QTR = 1/2 ∠QPR
Hence proved, ∠QTR = 1/2 ∠QPR.
☛ Check: NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6
Video Solution:
In Fig. 6.44, the side QR of △PQR is produced to a point S. If the bisectors of ∠PQR and ∠PRS meet at point T, then prove that ∠QTR = 1/2 ∠QPR.
NCERT Maths Solutions Class 9 Chapter 6 Exercise 6.3 Question 6
Summary:
In Fig. 6.44, if the side QR of △PQR is produced to a point S and the bisectors of ∠PQR and ∠PRS meet at point T, then it is proved that ∠QTR = 1/2 ∠QPR.
☛ Related Questions:
- In Fig. 6.40, ∠X = 62°, ∠XYZ = 54°. If YO and ZO are the bisectors of ∠XYZ and ∠XZY respectively of ∠XYZ, find ∠OZY and ∠YOZ.
- In Fig. 6.41, if AB || DE, ∠BAC = 35° and ∠CDE = 53°, find ∠DCE.
- In Fig. 6.42, if lines PQ and RS intersect at point T, such that ∠PRT = 40°, ∠RPT = 95° and ∠TSQ = 75°, find ∠SQT.
- In Fig. 6.43, if PQ ⊥ PS, PQ || SR, ∠SQR = 28° and ∠QRT = 65° then find the values of x and y.
visual curriculum
