Pythagoras Theorem
The Pythagoras theorem which is also referred to as the Pythagorean theorem explains the relationship between the three sides of a right-angled triangle. According to the Pythagorean theorem, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides of a triangle. Let us learn more about the Pythagoras theorem, the Pythagoras theorem formula, and the proof of Pythagoras theorem along with examples.
What is the Pythagoras Theorem?
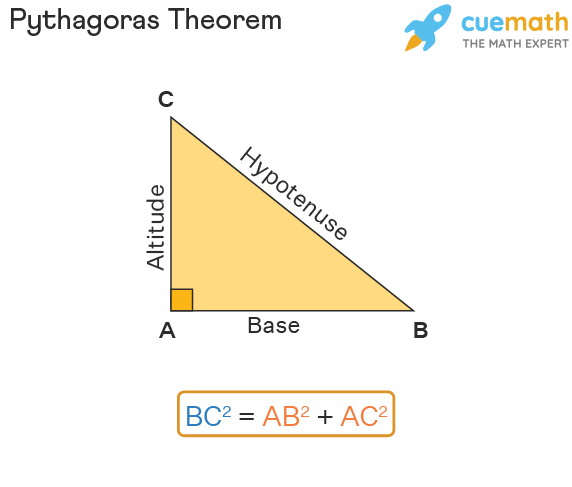
The Pythagoras theorem states that if a triangle is a right-angled triangle, then the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. Observe the following triangle ABC, in which we have BC2 = AB2 + AC2. Here, AB is the base, AC is the altitude (height), and BC is the hypotenuse. It is to be noted that the hypotenuse is the longest side of a right-angled triangle.
Pythagoras Theorem Equation
The Pythagoras theorem equation is expressed as, c2 = a2 + b2, where 'c' = hypotenuse of the right triangle and 'a' and 'b' are the other two legs. Hence, any triangle with one angle equal to 90 degrees produces a Pythagoras triangle and the Pythagoras equation can be applied in the triangle.
History of Pythagoras Theorem
Pythagoras theorem was introduced by the Greek Mathematician Pythagoras of Samos. He was an ancient Greek philosopher who formed a group of mathematicians who worked religiously on numbers and lived like monks. Although Pythagoras introduced the theorem, there is evidence that proves that it existed in other civilizations too, 1000 years before Pythagoras was born. The oldest known evidence is seen between the 20th to the 16th century B.C in the Old Babylonian Period.
Pythagoras Theorem Formula
The Pythagorean theorem formula states that in a right triangle ABC, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two legs. If AB and AC are the sides and BC is the hypotenuse of the triangle, then: BC2 = AB2 + AC2. In this case, AB is the base, AC is the altitude or the height, and BC is the hypotenuse.
Another way to understand the Pythagorean theorem formula is using the following figure which shows that the area of the square formed by the longest side of the right triangle (the hypotenuse) is equal to the sum of the area of the squares formed by the other two sides of the right triangle.
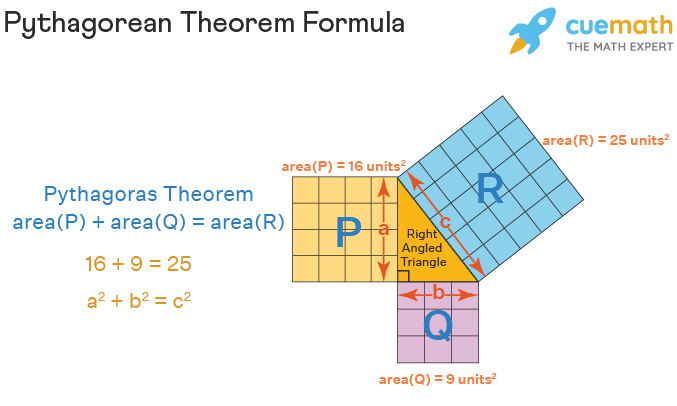
In a right-angled triangle, the Pythagoras Theorem Formula is expressed as:
c2 = a2 + b2
Where,
- 'c' = hypotenuse of the right triangle
- 'a' and 'b' are the other two legs.
Pythagoras Theorem Proof
The Pythagoras theorem can be proved in many ways. Some of the most common and widely used methods are the algebraic method and the similar triangles method. Let us have a look at both these methods individually in order to understand the proof of this theorem.
Proof of Pythagorean Theorem Formula using the Algebraic Method
The proof of the Pythagoras theorem can be derived using the algebraic method. For example, let us use the values a, b, and c as shown in the following figure and follow the steps given below:
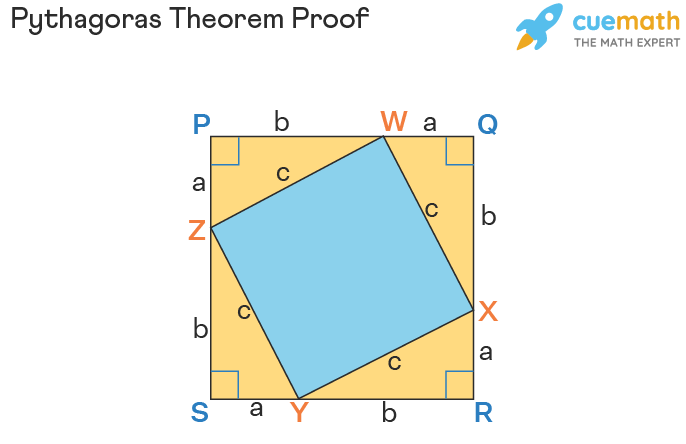
- Step 1: This method is also known as the 'proof by rearrangement'. Take 4 congruent right-angled triangles, with side lengths 'a' and 'b', and hypotenuse length 'c'. Arrange them in such a way that the hypotenuses of all the triangles form a tilted square. It can be seen that in the square PQRS, the length of the sides is 'a + b'. The four right triangles have 'b' as the base, 'a' as the height and, 'c' as the hypotenuse.
- Step 2: The 4 triangles form the inner square WXYZ as shown, with 'c' as the four sides.
- Step 3: The area of the square WXYZ by arranging the four triangles is c2.
- Step 4: The area of the square PQRS with side (a + b) = Area of 4 triangles + Area of the square WXYZ with side 'c'. This means (a + b)2 = [4 × 1/2 × (a × b)] + c2.This leads to a2 + b2 + 2ab = 2ab + c2. Therefore, a2 + b2 = c2. Hence, the Pythagoras theorem formula is proved.
Pythagorean Theorem Formula Proof using Similar Triangles
Two triangles are said to be similar if their corresponding angles are of equal measure and their corresponding sides are in the same ratio. Also, if the angles are of the same measure, then by using the sine law, we can say that the corresponding sides will also be in the same ratio. Hence, corresponding angles in similar triangles lead us to equal ratios of side lengths.
Derivation of Pythagorean Theorem Formula
Consider a right-angled triangle ABC, right-angled at B. Draw a perpendicular BD meeting AC at D.
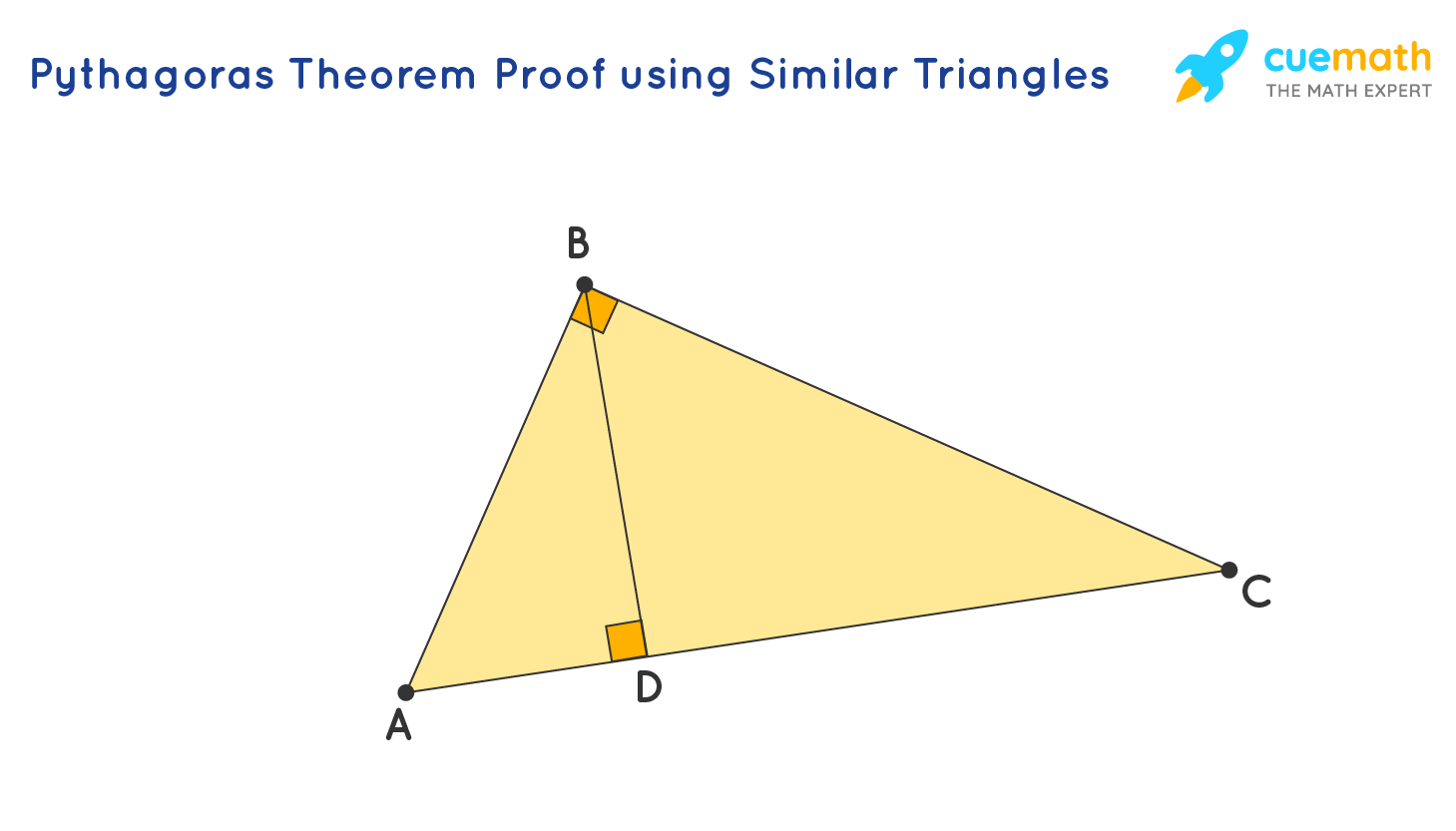
In △ABD and △ACB,
- ∠A = ∠A (common)
- ∠ADB = ∠ABC (both are right angles)
Thus, △ABD ∼ △ACB (by AA similarity criterion)
Similarly, we can prove △BCD ∼ △ACB.
Thus △ABD ∼ △ACB, Therefore, AD/AB = AB/AC. We can say that AD × AC = AB2.
Similarly, △BCD ∼ △ACB. Therefore, CD/BC = BC/AC. We can also say that CD × AC = BC2.
Adding these 2 equations, we get AB2 + BC2 = (AD × AC) + (CD × AC)
AB2 + BC2 =AC(AD +DC)
AB2 + BC2 =AC2
Hence proved.
Pythagoras Theorem Triangles
Right triangles follow the rule of the Pythagoras theorem and they are called Pythagoras theorem triangles. The three sides of such a triangle are collectively called Pythagoras triples. All the Pythagoras theorem triangles follow the Pythagoras theorem which says that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the two sides of the right-angled triangle. This can be expressed as c2 = a2 + b2; where 'c' is the hypotenuse and 'a' and 'b' are the two legs of the triangle.
Pythagoras Theorem Squares
As per the Pythagorean theorem, the area of the square which is built upon the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the area of the squares built upon the other two sides. These squares are known as Pythagoras squares.
Applications of Pythagoras Theorem
The applications of the Pythagoras theorem can be seen in our day-to-day life. Here are some of the applications of the Pythagoras theorem.
- Engineering and Construction fields
Most architects use the technique of the Pythagorean theorem to find the unknown dimensions. When the length or breadth is known it is very easy to calculate the diameter of a particular sector. It is mainly used in two dimensions in engineering fields.
- Face recognition in security cameras
The face recognition feature in security cameras uses the concept of the Pythagorean theorem, that is, the distance between the security camera and the location of the person is noted and well-projected through the lens using the concept.
- Woodwork and interior designing
The Pythagoras concept is applied in interior designing and the architecture of houses and buildings.
- Navigation
People traveling in the sea use this technique to find the shortest distance and route to proceed to their concerned places.
☛ Related ArticlesCuemath is one of the world's leading math learning platforms that offers LIVE 1-to-1 online math classes for grades K-12. Our mission is to transform the way children learn math, to help them excel in school and competitive exams. Our expert tutors conduct 2 or more live classes per week, at a pace that matches the child's learning needs.
Pythagorean Theorem Examples
-
Example 1: The hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle is 16 units and one of the sides of the triangle is 8 units. Find the measure of the third side using the Pythagoras theorem formula.
Solution:
Given: Hypotenuse = 16 units
Let us consider the given side of a triangle as the perpendicular height = 8 units
On substituting the given dimensions to the Pythagoras theorem formula
Hypotenuse2 = Base2 + Height2
162 = B2 + 82
B2 = 256 - 64
B = √192 = 13.856 units
Therefore, the measure of the third side of the triangle is 13.856 units.
-
Example 2: Julie wanted to wash her building window which is 12 feet off the ground. She has a ladder that is 13 feet long. How far should she place the base of the ladder away from the building?
Solution:
We can visualize this scenario as a right triangle. We need to find the base of the right triangle formed. We know that, Hypotenuse2 = Base2 + Height2. Thus, we can say that b2 = 132 - 122 where 'b' is the distance of the base of the ladder from the feet of the wall of the building. So, b2 = 132 - 122 can be solved as, b2 = 169 - 144 = 25. This means, b = √25 = 5. Hence, we get 'b' = 5.
Therefore, the base of the ladder is 5 feet away from the building.
-
Example 3: Use the Pythagoras theorem to find the hypotenuse of the triangle in which the sides are 8 units and 6 units respectively.
Solution:
Using the Pythagoras theorem, Hypotenuse2 = Base2 + Height2 = 82 + 62. This leads to Hypotenuse2 = 64 + 36 = 100. Therefore, hypotenuse = √100 = 10 units.
Therefore, the length of the hypotenuse is 10 units.

FAQs on Pythagoras Theorem
What is the Pythagoras Theorem in Math?
The Pythagoras theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. This theorem can be expressed as, c2 = a2 + b2; where 'c' is the hypotenuse and 'a' and 'b' are the two legs of the triangle. These triangles are also known as Pythagoras theorem triangles.
What is the Converse of Pythagoras Theorem?
The converse of Pythagoras theorem is: If the sum of the squares of any two sides of a triangle is equal to the square to the third (largest) side, then it is said to be a right-angled triangle.
What is the Use of the Pythagorean Theorem Formula?
The Pythagoras theorem works only for right-angled triangles. When any two values are known, we can apply the Pythagoras theorem and calculate the unknown sides of the triangle. There are other real-life applications of the Pythagoras theorem like in the field of navigation, engineering and architecture.
What is the use of the Pythagoras Theorem?
The Pythagorean theorem is used in various fields. A few of its applications are given below.
- Architecture, construction and Navigation industries.
- For computing the distance between points on the plane.
- For calculating the perimeter, the surface area, the volume of geometrical shapes, and so on.
Can the Pythagorean Theorem Formula be Applied to any Triangle?
No, the Pythagorean theorem can only be applied to a right-angled triangle since the Pythagorean theorem expresses the relationship between the sides of the triangle where the square of the two legs is equal to the square of the third side which is the hypotenuse.
How to Work Out the Pythagoras Theorem?
Pythagoras theorem can be used to find the unknown side of a right-angled triangle. For example, if two legs of a right-angled triangle are given as 4 units and 6 units, then the hypotenuse (the third side) can be calculated using the formula, c2 = a2 + b2; where 'c' is the hypotenuse and 'a' and 'b' are the two legs. Substituting the values in the formula, c2 = a2 + b2 = c2 = 42 + 62 = 16 + 36 = √52 = 7.2 units.
What is the Formula of Pythagoras Theorem?
The formula of Pythagoras theorem is expressed as, Hypotenuse2 = Base2 + Height2. This is also written as, c2 = a2 + b2; where 'c' is the hypotenuse and 'a' and 'b' are the two legs of the right-angled triangle. Using the Pythagoras theorem formula, any unknown side of a right-angled can be calculated if the other two sides are given.
Why is the Pythagoras Theorem Important?
The Pythagoras theorem is important because it helps in calculating the unknown side of a right-angled triangle. It has other real-life applications in the field of architecture and engineering, navigation, and so on.
How is Pythagoras Theorem used in Navigation?
The Pythagoras theorem is commonly used in air navigation and ship navigation. The Pythagoras theorem provides a way to the ship's navigator to calculate the distance to a point in the ocean, for example, if the distance between two points is given as 600 km north and 800 km west, the required distance can be calculated using the Pythagoras theorem.
When is Pythagoras Theorem used?
Pythagoras theorem is used when any two sides of a right-angled triangle are given and the third side needs to be calculated. For example, if the perpendicular and base of a right-angled triangle are given as 12 units and 5 units respectively, and we need to find the third side (the hypotenuse) we can calculate it using the theorem which says hypotenuse2 = perpendicular2 + base2. After substituting the values in the equation we get hypotenuse2 = 122 + 52 = 144 + 25 = 169. So, hypotenuse = √169 = 13 units.
What is the Pythagoras Property of Triangles?
The Pythagoras property of triangles is another term for the Pythagoras theorem. According to the Pythagoras property, in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is always equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. This theorem is expressed as, c2 = a2 + b2; where 'c' is the hypotenuse and 'a' and 'b' are the two legs of the triangle.
visual curriculum
