Internal Division
Introduction:
In this section, we are going to explore how to divide internally the given line segment in a given ratio by construction. Also, we are going to use the Basic Proportionality Theorem which states that "If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio".
Internal Division:
You are given a line segment \(AB\):
How will you divide it into a given (rational) ratio? Suppose that you are asked to internally divide \(AB\) in the ratio \(3:4\) . This means that you have to find a point \(C\) on \(AB\) such that \(AC:CB = 3:4\) , as shown below:
How will you geometrically locate point \(C\)? This is the problem of the internal division of a given line segment in a given ratio. We are going to use BPT to guide our construction.
Solved Example:
Example 1: Divide \(AB\) of any length in the ratio \(3:4\) internally.
Solution: Let us follow the steps of construction as given below:
Steps of construction for internal division:
Step 1: Draw a line segment \(AB\) of any length.
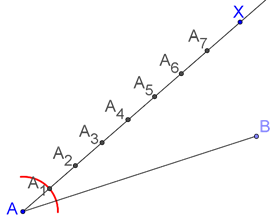
Step 2: Draw any ray \(AX\) inclined at an arbitrary angle to \(AB\) , and mark \(3 + 4 = 7\) equal intervals on \(AX\) , as shown below:
This can be done easily using a compass. In the figure, we have shown one arc (to construct the first interval)
Step 3: Join the last point (in this case, \({A_7}\) ) to B:
Step 4: Through \({A_3}\) , draw a parallel to \({A_7}B\) . The point of intersection of this parallel with \(AB\) is the required point \(C\):
The proof is straightforward.
We have \({A_3}C\parallel {A_7}B\) . Applying BPT in \(\Delta AB{A_7}\) , we have:
\[\frac{{A{A_3}}}{{{A_3}{A_7}}} = \frac{{AC}}{{CB}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \boxed{\frac{{AC}}{{CB}} = \frac{3}{4}}\]
✍Note: Using this approach, we can divide any given segment in an arbitrary rational ratio.
Challenge: Construct some line segments and divide them into the following ratios:
\[3:5,{\text{ }}2:3,{\text{ }}1:7,{\text{ }}6:7,{\text{ }}2:11\]
⚡Tip: Use the same steps of construction as we have used in the above example.