Null Hypothesis
Null hypothesis is used to make decisions based on data and by using statistical tests. Null hypothesis is represented using Ho and it states that there is no difference between the characteristics of two samples. Null hypothesis is generally a statement of no difference. The rejection of null hypothesis is equivalent to the acceptance of the alternate hypothesis.
Let us learn more about null hypotheses, tests for null hypotheses, the difference between null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis, with the help of examples, FAQs.
| 1. | What Is Nulll Hypothesis? |
| 2. | Tests for Null Hypothesis |
| 3. | Difference Between Null Hypothesis And Alternate Hypothesis |
| 4. | FAQs on Null Hypothesis |
What Is Null Hypothesis?
Null hypothesis states that there is no significant difference between the observed characteristics across two sample sets. Null hypothesis states the observed population parameters or variables is the same across the samples. The null hypothesis states that there is no relationship between the sample parameters, the independent variable, and the dependent variable. The term null hypothesis is used in instances to mean that there is no differences in the two means, or that the difference is not so significant.
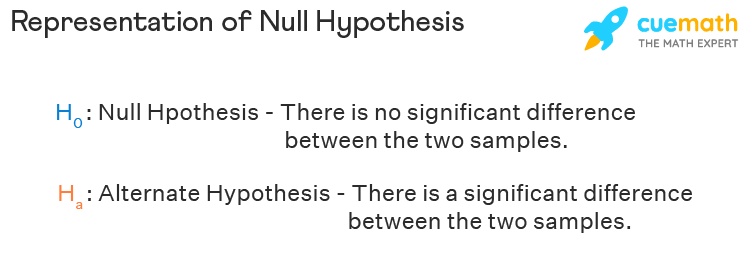
If the experimental outcome is the same as the theoretical outcome then the null hypothesis holds good. But if there are any differences in the observed parameters across the samples then the null hypothesis is rejected, and we consider an alternate hypothesis. The rejection of the null hypothesis does not mean that there were flaws in the basic experimentation, but it sets the stage for further research. Generally, the strength of the evidence is tested against the null hypothesis.
Null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis are the two approaches used across statistics. The alternate hypothesis states that there is a significant difference between the parameters across the samples. The alternate hypothesis is the inverse of null hypothesis. An important reason to reject the null hypothesis and consider the alternate hypothesis is due to experimental or sampling errors.
Tests For Null Hypothesis
The two important approaches of statistical interference of null hypothesis are significance testing and hypothesis testing. The null hypothesis is a theoretical hypothesis and is based on insufficient evidence, which requires further testing to prove if it is true or false.
Significance Testing
The aim of significance testing is to provide evidence to reject the null hypothesis. If the difference is strong enough then reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternate hypothesis. The testing is designed to test the strength of the evidence against the hypothesis. The four important steps of significance testing are as follows.
- First state the null and alternate hypotheses.
- Calculate the test statistics.
- Find the p-value.
- Test the p-value with the α and decide if the null hypothesis should be rejected or accepted.
If the p-value is lesser than the significance level α, then the null hypothesis is rejected. And if the p-value is greater than the significance level α, then the null hypothesis is accepted.
Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing takes the parameters from the sample and makes a derivation about the population. A hypothesis is an educated guess about a sample, which can be tested either through an experiment or an observation. Initially, a tentative assumption is made about the sample in the form of a null hypothesis.
There are four steps to perform hypothesis testing. They are:
- Identify the null hypothesis.
- Define the null hypothesis statement.
- Choose the test to be performed.
- Accept the null hypothesis or the alternate hypothesis.
There are often errors in the process of testing the hypothesis. The two important errors observed in hypothesis testing is as follows.
- Type - I error is rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is actually true.
- Type - II error is accepting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is actually false.
Difference Between Null Hypothesis And Alternate Hypothesis
The difference between null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis can be understood through the following points.
- The opposite of the null hypothesis is the alternate hypothesis and it is the claim which is being proved by research to be true.
- The null hypothesis states that the two samples of the population are the same, and the alternate hypothesis states that there is a significant difference between the two samples of the population.
- The null hypothesis is designated as Ho and the alternate hypothesis is designated as Ha.
- For the null hypothesis, the same means are assumed to be equal, and we have H0: µ1= µ2. And for the alternate hypothesis, the sample means are unequal, and we have Ha: µ1≠ µ2.
- The observed population parameters and variables are the same across the samples, for a null hypothesis, but in an alternate hypothesis, there is a significant difference between the observed parameters and variables across the samples.
☛ Related Topics
The following topics help in a better understanding of the null hypothesis.
Examples on Null Hypothesis
-
Example 1: A medical experiment and trial is conducted to check if a particular drug can serve as the vaccine for Covid-19, and can prevent from occurrence of Corona. Write the null hypothesis and the alternate hypothesis for this situation.
Solution:
The given situation refers to a possible new drug and its effectiveness of being a vaccine for Covid-19 or not. The null hypothesis (Ho) and alternate hypothesis (Ha) for this medical experiment is as follows.
- H0: The use of the new drug is not helpful for the prevention of Covid-19.
- Ha: The use of the new drug serves as a vaccine and helps for the prevention of Covid-19.
-
Example 2: The teacher has prepared a set of important questions and informs the student that preparing these questions helps in scoring more than 60% marks in the board exams. Write the null hypothesis and the alternate hypothesis for this situation.
Solution:
The given situation refers to the teacher who has claimed that her important questions helps to score more than 60% marks in the board exams. The null hypothesis(Ho) and alternate hypothesis(Ha) for this situation is as follows.
- Ho: The important questions given by the teacher does not really help the students to get a score of more than 60% in the board exams.
- Ha: The important questions given by the teacher is helpful for the students to score more than 60% marks in the board exams.

FAQs on Null Hypothesis
What is Null Hypothesis In Maths?
Null hypothesis is used in statistics and it states if there is any significant difference between the two samples. The acceptance of null hypothesis mean that there is no significant difference between the two samples. And the rejection of null hypothesis means that the two samples are different, and we need to accept the alternate hypothesis. The null hypothesis statement is represented as H0 and the alternate hypothesis is represented as Ha.
How Do You Test Null Hypothesis?
The null hypothesis is broadly tested using two methods. The null hypothesis can be tested using significance testing and hypothesis testing.Broadly the test for null hypothesis is performed across four stages. First the null hypothesis is identified, secondly the null hypothesis is defined. Next a suitable test is used to test the hypothesis, and finally either the null hypothesis or the alternate hypothesis is accepted.
How To Accept or Reject Null Hypothesis?
The null hypothesis is accepted or rejected based on the result of the hypothesis testing. The p value is found and the significance level is defined. If the p-value is lesser than the significance level α, then the null hypothesis is rejected. And if the p-value is greater than the significance level α, then the null hypothesis is accepted.
What Is the Difference Between Null Hypothesis And Alternate Hypothesis?
The null hypothesis states that there is no significant difference between the two samples, and the alternate hypothesis states that there is a significant difference between the two samples. The null hypothesis is referred using Ho and the alternate hypothesis is referred using Ha. As per null hypothesis the observed variables and parameters are the same across the samples, but as per alternate hypothesis there is a significant difference between the observed variables and parameters across the samples.
What Is Null Hypothesis Example?
A few quick examples of null hypothesis are as follows.
- The salary of a person is independent of his profession, is an example of null hypothesis. And the salary is dependent on the profession of a person, is an alternate hypothesis.
- The performance of the students in Maths from two different classes is a null hypothesis. And the performance of the students from each of the classes is different, is an example of alternate hypothesis.
- The nutrient content of mango and a mango milk shake is equal and it can be taken as a null hypothesis. The test to prove the different nutrient content of the two is referred to as alternate hypothesis.
visual curriculum
