Common Difference
Common difference is a concept used in sequences and arithmetic progressions. The celebration of people's birthdays can be considered as one of the examples of sequence in real life. In this example, the common difference between consecutive celebrations of the same person is one year.
In this article, let's learn about common difference, and how to find it using solved examples.
| 1. | What is Common Difference? |
| 2. | Common Difference Formula |
| 3. | Finding Common Difference in Arithmetic Progression (AP) |
| 4. | Examples on Common Difference |
| 5. | FAQs on Common Difference |
What is Common Difference?
The common difference of an arithmetic sequence is the difference between any of its terms and its previous term. An arithmetic sequence goes from one term to the next by always adding (or subtracting) the same amount. The number added (or subtracted) at each stage of an arithmetic sequence is called the "common difference", because if we subtract (that is if you find the difference of) successive terms, you'll always get this common value. Most often, "d" is used to denote the common difference.
Consider the arithmetic sequence: 2, 4, 6, 8,..
Here, the common difference between each term is 2 as:
- 2nd term - 1st term = 4 - 2 = 2
- 3rd term - 2nd term = 6 - 4 = 2
- 4th term - 3rd term = 8 - 6 = 2
and so on.
Thus, the common difference is the difference "latter - former" (NOT former - latter).
Common Difference Formula
The common difference is the value between each successive number in an arithmetic sequence. Therefore, the formula to find the common difference of an arithmetic sequence is: d = a(n) - a(n - 1), where a(n) is nth term in the sequence, and a(n - 1) is the previous term (or (n - 1)th term) in the sequence. There are two kinds of arithmetic sequence:
- Increasing arithmetic sequence: In this, the common difference is positive
- Decreasing arithmetic sequence: In this, the common difference is negative
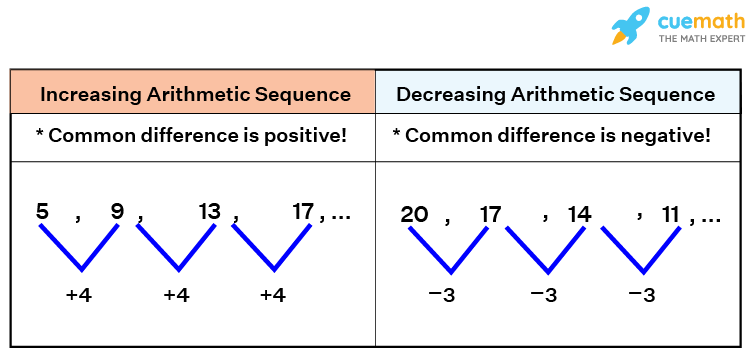
Some sequences are made up of simply random values, while others have a fixed pattern that is used to arrive at the sequence's terms. The arithmetic sequence (or progression), for example, is based upon the addition of a constant value to reach the next term in the sequence. The number added to each term is constant (always the same).
a1, (a1 + d), (a1 + 2d), ...
The fixed amount is called the common difference, d, referring to the fact that the difference between two successive terms generates the constant value that was added. To find the common difference, subtract the first term from the second term. Such terms form a linear relationship.

Arithmetic sequences have a linear nature when plotted on graphs (as a scatter plot). The domain consists of the counting numbers 1, 2, 3, 4,5 ... (representing the location of each term) and the range consists of the actual terms of the sequence. In the graph shown above, while the x-axis increased by a constant value of one, the y value increased by a constant value of 3. Hence, the above graph shows the arithmetic sequence 1, 4, 7, 10, 13, and 16.
Finding Common Difference in Arithmetic Progression (AP)
Let's make an arithmetic progression with a starting number of 2 and a common difference of 5.
- Our first term will be our starting number: 2. Our second term = the first term (2) + the common difference (5) = 7.
- So the first two terms of our progression are 2, 7. Our third term = second term (7) + the common difference (5) = 12.
- So the first three terms of our progression are 2, 7, 12. Our fourth term = third term (12) + the common difference (5) = 17.
- So the first four terms of our progression are 2, 7, 12, 17.
Now we are familiar with making an arithmetic progression from a starting number and a common difference. Now, let's learn how to find the common difference of a given sequence. 2,7,12,..
- The first term here is 2; so that is the starting number.
- The second term is 7. To find the difference between this and the first term, we take 7 - 2 = 5. So the difference between the first and second terms is 5.
- The second term is 7 and the third term is 12. To find the difference, we take 12 - 7 which gives us 5 again. So the common difference between each term is 5.
The below-given table gives some more examples of arithmetic progressions and shows how to find the common difference of the sequence.
| Arithmetic Progression (AP) | Common Difference 'd' |
|---|---|
| 1, 6, 11, 16, 21, 26, ... | d = 5; 5 is added to each term to arrive at the next term. So d = a2 - a1 = 6 - 1 = 5. |
| 10, 8, 6, 4, 2, 0, -2, -4, -6,.. | d = -2; -2 is added to each term to arrive at the next term. So d = a2 - a1 = 8 - 10 = -2. |
| 1, 1/2, 0, -1/2,.. | d = -½; -½ is added to each term to arrive at the next term. So d = a2 - a1 = ½ - 1 = -½. |
Important Notes on Common Difference:
Here is a list of a few important points related to common difference.
- An arithmetic sequence goes from one term to the next by always adding or subtracting the same amount.
- The number added or subtracted at each stage of an arithmetic sequence is called the "common difference"
- The common difference is denoted by 'd' and is found by finding the difference any term of AP and its previous term.
☛ Related Topics:
Check out the following pages related to Common Difference
Examples of Common Difference
-
Example 1: Determine the common difference in the given sequence: -3, 0, 3, 6, 9, 12, ...
Solution:
Given sequence: -3, 0, 3, 6, 9, 12, ...
The common difference is the distance between each number in the sequence. Notice that each number is 3 away from the previous number.
12 − 9 = 3
9 − 6 = 3
6 − 3 = 3
3 − 0 = 3
0 −(−3) = 3Thus, the common difference is 3.
Answer: 3
-
Example 2: What is the common difference in the following sequence?
3, 11,19, 27, 35...
Solution:
Given sequence: 3, 11,19, 27, 35...
To find the common difference, simply subtract the first term from the second term, or the second from the third, or so on...
11−3 = 8
19−11 = 8
Clearly, each time we are adding 8 to get to the next term. Thus, the common difference is 8.Answer:8
-
Example 3: If 100th term of an arithmetic progression is -15.5 and the common difference is -0.25, then find its 102nd term.
Solution:
It is given that d = -0.25.
101st term = 100th term + d = -15.5 + (-0.25) = -15.75
102nd term = 101st term + d = -15.75 + (-0.25) = -16
Answer: -16

FAQs on Common Difference
What is the Common Difference of Any Arithmetic Sequence?
The common difference of an arithmetic sequence is the difference between two consecutive terms. It is denoted by 'd' and is found by using the formula, d = a(n) - a(n - 1). Here,
- a(n) = any term (nth term)
- a(n - 1) = the previous term of a(n)
How to Find the Common Difference of Arithmetic Sequence?
The common difference is the difference between every two numbers in an arithmetic sequence.
- Step 1: Take any two consecutive terms.
- Step 2: Find their difference, d = a(n) - a(n - 1), where a(n) is a term in the sequence, and a(n - 1) is the previous term of a(n).
Can the Common Difference of AP Be Negative?
Yes, the common difference of an arithmetic progression (AP) can be positive, negative, or even zero. In a decreasing arithmetic sequence, the common difference is always negative as such a sequence starts out negative and keeps descending.
Can the Common Difference in AP Be Zero?
Yes. The common difference in an arithmetic progression can be zero. As per the definition of an arithmetic progression (AP), a sequence of terms is considered to be an arithmetic sequence if the difference between the consecutive terms is constant. Thus, an AP may have a common difference of 0. And since 0 is a constant, it should be included as a common difference, but it kinda feels wrong for all the numbers to be equal while being in an arithmetic progression.
What is the Symbol of Common Difference?
The common difference is the value between each term in an arithmetic sequence and it is denoted by the symbol 'd'.
What if the Common Difference Is Not Constant?
In a sequence, if the common difference of the consecutive terms is not constant, then the sequence cannot be considered as arithmetic.
What is the Common Difference Formula?
The formula to find the common difference of an arithmetic sequence is: d = a(n) - a(n - 1), where a(n) is a term in the sequence, and a(n - 1) is its previous term in the sequence.
visual curriculum
