GCF of 2 and 5
GCF of 2 and 5 is the largest possible number that divides 2 and 5 exactly without any remainder. The factors of 2 and 5 are 1, 2 and 1, 5 respectively. There are 3 commonly used methods to find the GCF of 2 and 5 - Euclidean algorithm, long division, and prime factorization.
| 1. | GCF of 2 and 5 |
| 2. | List of Methods |
| 3. | Solved Examples |
| 4. | FAQs |
What is GCF of 2 and 5?
Answer: GCF of 2 and 5 is 1.
Explanation:
The GCF of two non-zero integers, x(2) and y(5), is the greatest positive integer m(1) that divides both x(2) and y(5) without any remainder.
Methods to Find GCF of 2 and 5
Let's look at the different methods for finding the GCF of 2 and 5.
- Using Euclid's Algorithm
- Long Division Method
- Listing Common Factors
GCF of 2 and 5 by Euclidean Algorithm
As per the Euclidean Algorithm, GCF(X, Y) = GCF(Y, X mod Y)
where X > Y and mod is the modulo operator.
Here X = 5 and Y = 2
- GCF(5, 2) = GCF(2, 5 mod 2) = GCF(2, 1)
- GCF(2, 1) = GCF(1, 2 mod 1) = GCF(1, 0)
- GCF(1, 0) = 1 (∵ GCF(X, 0) = |X|, where X ≠ 0)
Therefore, the value of GCF of 2 and 5 is 1.
GCF of 2 and 5 by Long Division
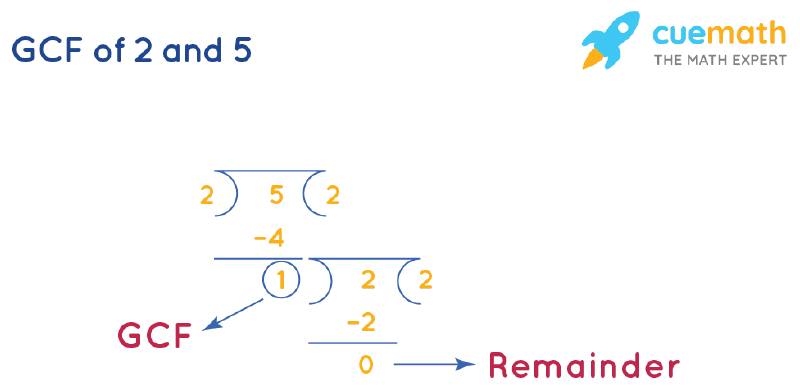
GCF of 2 and 5 is the divisor that we get when the remainder becomes 0 after doing long division repeatedly.
- Step 1: Divide 5 (larger number) by 2 (smaller number).
- Step 2: Since the remainder ≠ 0, we will divide the divisor of step 1 (2) by the remainder (1).
- Step 3: Repeat this process until the remainder = 0.
The corresponding divisor (1) is the GCF of 2 and 5.
GCF of 2 and 5 by Listing Common Factors
- Factors of 2: 1, 2
- Factors of 5: 1, 5
Since, 1 is the only common factor between 2 and 5. The Greatest Common Factor of 2 and 5 is 1.
☛ Also Check:
- GCF of 40 and 50 = 10
- GCF of 45 and 60 = 15
- GCF of 34 and 85 = 17
- GCF of 3 and 9 = 3
- GCF of 18 and 28 = 2
- GCF of 18 and 27 = 9
- GCF of 7 and 21 = 7
GCF of 2 and 5 Examples
-
Example 1: Find the GCF of 2 and 5, if their LCM is 10.
Solution:
∵ LCM × GCF = 2 × 5
⇒ GCF(2, 5) = (2 × 5)/10 = 1
Therefore, the greatest common factor of 2 and 5 is 1. -
Example 2: For two numbers, GCF = 1 and LCM = 10. If one number is 2, find the other number.
Solution:
Given: GCF (x, 2) = 1 and LCM (x, 2) = 10
∵ GCF × LCM = 2 × (x)
⇒ x = (GCF × LCM)/2
⇒ x = (1 × 10)/2
⇒ x = 5
Therefore, the other number is 5. -
Example 3: The product of two numbers is 10. If their GCF is 1, what is their LCM?
Solution:
Given: GCF = 1 and product of numbers = 10
∵ LCM × GCF = product of numbers
⇒ LCM = Product/GCF = 10/1
Therefore, the LCM is 10.

FAQs on GCF of 2 and 5
What is the GCF of 2 and 5?
The GCF of 2 and 5 is 1. To calculate the GCF (Greatest Common Factor) of 2 and 5, we need to factor each number (factors of 2 = 1, 2; factors of 5 = 1, 5) and choose the greatest factor that exactly divides both 2 and 5, i.e., 1.
If the GCF of 5 and 2 is 1, Find its LCM.
GCF(5, 2) × LCM(5, 2) = 5 × 2
Since the GCF of 5 and 2 = 1
⇒ 1 × LCM(5, 2) = 10
Therefore, LCM = 10
☛ GCF Calculator
How to Find the GCF of 2 and 5 by Prime Factorization?
To find the GCF of 2 and 5, we will find the prime factorization of the given numbers, i.e. 2 = 2; 5 = 5.
⇒ There is no common prime factor for 2 and 5. Hence, GCF (2, 5) = 1.
☛ What are Prime Numbers?
What is the Relation Between LCM and GCF of 2, 5?
The following equation can be used to express the relation between LCM and GCF of 2 and 5, i.e. GCF × LCM = 2 × 5.
How to Find the GCF of 2 and 5 by Long Division Method?
To find the GCF of 2, 5 using long division method, 5 is divided by 2. The corresponding divisor (1) when remainder equals 0 is taken as GCF.
What are the Methods to Find GCF of 2 and 5?
There are three commonly used methods to find the GCF of 2 and 5.
- By Long Division
- By Prime Factorization
- By Euclidean Algorithm
visual curriculum
