Mass
Mass is the amount of matter present in any object or body. Everything we see around us has mass. For example, a table, a chair, your bed, a football, a glass, and even air has mass. This means all objects are light or heavy because of their mass. In this lesson, we will learn what is mass, how to calculate mass, and its examples while discovering interesting facts about it. SEO-Mass-Item1
| 1. | What is Mass? |
| 2. | What is the Unit of Mass? |
| 3. | Difference Between Mass and Weight |
| 4. | FAQs on Mass |
What is Mass?
In Physics, mass is the most basic property of matter and it is one of the fundamental quantities. Mass is defined as the amount of matter present in a body. The SI unit of mass is the kilogram (kg).
Mass Definition
The definition of mass says that mass is a quantity that represents the amount of matter in a particle or an object.
Note: The mass of a body is constant; it does not change at any time. Only in certain extreme cases when a huge amount of energy is given or taken from a body, the mass may be impacted. For example, in a nuclear reaction, a tiny amount of matter is converted into a huge amount of energy, which reduces the mass of the substance.
Mass Formula
The mass of an object can be calculated using different formulas depending on the parameters given.
- The first formula of mass is expressed as, Mass = Density × Volume. This means if we know the density and volume of an object, we can find its mass using this formula of mass.
- The second formula of mass is expressed as, Mass = Force ÷ Acceleration. This means if we know the force and acceleration of an object, we can find its mass using this formula of mass.
- The third formula of mass is expressed as, Mass = Weight ÷ Gravitational Acceleration. This means if we know the weight of an object and the gravitational acceleration, we can find its mass using this formula of mass.
What is the Unit of Mass?
There are various units for calculating mass, like, kilograms, grams, lbs, pounds, etc., but the SI unit of mass is 'kilogram' or kg. Every unit of mass can be converted to other units by using a proper conversion formula without affecting the meaning and essence of the quantity to be measured.
Note: 1kg is equal to 2.20462 pounds.
Difference Between Mass and Weight
People often get confused between mass and weight and they end up using these two terms interchangeably. However, mass and weight are two different terms and it is important to understand the difference between them. The difference between mass and weight is shown in the table given below.
| Mass | Weight | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mass is defined as the amount of matter in a substance | Weight is defined as the amount of force acting on the mass of an object because of acceleration due to gravity. |
| Denotation | Mass is represented by 'M' |
Weight is represented by 'W' |
| Formula | •Mass is always constant for a body. •One way to calculate mass: Mass = volume × density |
•Weight is the measure of the gravitational force acting on a mass. •Formula of weight: Weight = mass × acceleration due to gravity |
| Unit of Measurement | The SI unit of mass is 'kilogram' | The SI unit of weight is Newton (N). |
| Quantity Type | •Mass is a base quantity. •Mass only has magnitude and hence, it is a scalar quantity |
•Weight is a derived quantity. •Weight has both magnitude and direction (toward the center of gravity) and hence, it is a vector quantity. |
| Measuring Instrument | Mass can be easily measured using any ordinary balance. For example, beam balance, lever balance, pan balance, etc. |
Weight can be measured by a spring balance or by using the formula given above. |
Did you know that we have different weights on the Earth, the Moon, and in space? However, our mass is the same everywhere.
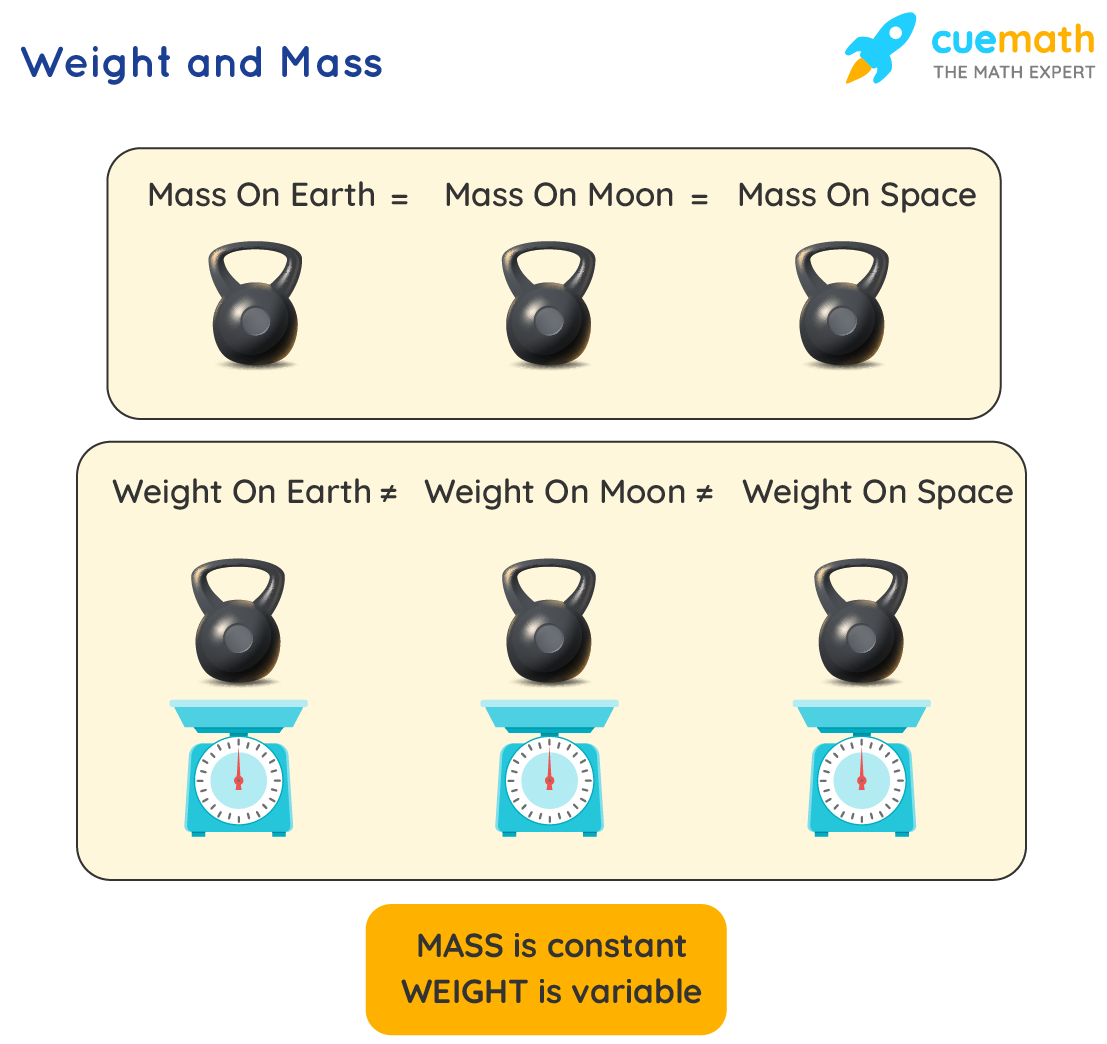
Now, let us look at some important facts related to mass.
- Mass only has magnitude, hence, it is a scalar quantity.
- Weight has both magnitude and direction; it is a vector quantity.
- Mass can also be defined as the 'stored energy in particles'
- Mass represents the total atoms or particles that it contains.
☛Related Links
Solved Examples of Mass
-
Example 1: State true or false with reference to mass. a.) Mass is always constant for a body. b.) The SI unit of mass is Newton
Solution: a.) True, mass is always constant for a body. b.) False, the SI unit of mass is Kilograms.
-
Example 2: The mass of an object is 6,000 pounds. Calculate its mass in tons.
Solution: We know that 1 ton = 2000 pounds. Thus, 6000 pounds = 6000/2000 = 3 tons.
-
Example 3: Damian has a book that has a mass of 2.2 kg. What is the weight of the book on the Earth?
Solution:
Mass of textbook = 2.2 kg and acceleration due to gravity = 9.8 m/s2
Weight formula = Mass × Acceleration due to gravity
Weight of textbook = 2.2 × 9.8
Weight of textbook = 21.56 N
Therefore, the weight of the textbook on Earth is 21.56 N.

FAQs on Mass
What is Mass?
The definition of mass says that mass is a quantity that represents the amount of matter in a particle or an object. In other words, everything we see around us has mass and all objects are light or heavy because of their mass. The SI unit of mass is kilograms.
How to Find Mass?
The mass of an object can be measured using any ordinary balance. For example, beam balance, lever balance, pan balance, etc. It can also be calculated using the formula, Mass = volume × density. This means if we know the volume and density of an object we can easily find its mass. Apart from this, there are other formulas that help in calculating the mass of an object, for example, Mass = Force ÷ Acceleration and Mass = Weight ÷ Gravitational Acceleration
What is the Mass Formula?
The mass of an object can be calculated using different formulas depending on the known values.
- The first formula of mass is expressed as, Mass = Density × Volume. This means if we know the density and volume of an object, we can find its mass using this formula of mass.
- The second formula of mass is expressed as, Mass = Force ÷ Acceleration. This means if we know the force and acceleration of an object, we can find its mass using this formula of mass.
- The third formula of mass is expressed as, Mass = Weight ÷ Gravitational Acceleration. This means if we know the weight of an object and the gravitational acceleration, we can find its mass using this formula of mass.
Does Air Have Mass?
Yes, the air has mass. For example, an inflated balloon weighs heavier than a deflated balloon, which proves that the air inside the inflated balloon has mass.
Are Mass and Volume the Same?
No, mass is the amount of matter that an object is made up of. Volume is the amount of vacant space that an object takes up. Hence, mass and volume are not the same.
Are Weight and Mass the Same?
No, weight and mass are not the same. Weight is the amount of force acting on a body and mass is the amount of matter in a body. Weight can be changed depending upon the force while mass is constant. The SI unit of weight is Newton, while the SI unit of mass is kilograms.
What is the S.I Unit of Mass?
The S.I Unit of Mass is Kilograms (kg). This means that the mass of an object is expressed in kilograms. For example, we can say that the mass of an object is 36 kilograms.
What is the Mass Equation?
The mass equation is another name for the mass formula. And there are different formulas for calculating the mass of an object.
- If we know the density and volume of an object, we can find its mass using the formula: Mass = Density × Volume
- If we know the force and acceleration of an object, we can find its mass using the formula: Mass = Force ÷ Acceleration
- If we know the weight of an object and the gravitational acceleration, we can find its mass using the formula: Mass = Weight ÷ Gravitational Acceleration
visual curriculum
